Porcine clonorchiasis prevention and treatment technology
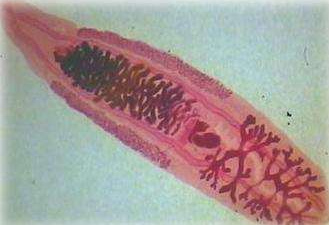
Clostridium is a trematode caused by parasitic clonorchiasis (Clonorchissinensis) in the genus Bacterial. In addition to pigs, it is also parasitic in the gallbladder and bile ducts of human livers such as humans, dogs, cats, baboons, baboons, etc., which can cause liver enlargement and cause other liver diseases. It is an important zoonotic parasitic disease. Pathogen form The worm body has a flat leaf shape with a slightly pointed front end and a blunt back end. The mouth suction cup is slightly larger than the abdominal suction cup. The two cecums reach the back end of the worm. Two branched testes are arranged in the posterior 1/3 of the worm. Ovarian lobes, located before the testicles. The fertilized sac is developed in an elliptical shape between the testicle and the ovary. The sac is curved in an "S" shape, at the back of the worm. The eggs are very small, with an average of 29 μm × 17 μm, resembling an electric bulb, with an egg cover at the upper end and a small protrusion at the rear end, containing the hairy mites. [life history] The development of Clonorchis sinensis requires freshwater snails as the first intermediate host, and freshwater fish and shrimp as the second intermediate host. The eggs produced by adults enter the digestive tract and are excreted in the feces. If they fall into the water and are swallowed by the first intermediate host, they can hatch the mites in the digestive tract of the snail. The ranunculus enters the lymphatic system and liver of the snail and develops into cytoplasm, thunder and scorpion. Mature cercaria leaves the snail and swims in the water, such as encountering a suitable second intermediate host - some freshwater fish and shrimp, which penetrate into their muscles to form a sac. People, pigs, dogs and cats are infected by swallowing raw fish, shrimp or uncooked fish or shrimp containing cystic mites. The cystic sac is decapsulated in the duodenum, and the child worm moves along the bile flow in the opposite direction, and reaches the bile duct through the common bile duct to develop into an adult worm. It takes about 100 days to eat the eggs from the freshwater snails to the scorpion. The larvae develop into adults in the terminal host after 1 month. Epidemiology The prevalence of this disease is closely related to the geographical environment, natural conditions, and living habits. There is a source of infection; in the epidemic area, toilets are built on fish ponds, and fish are used to feed fish; there are a large number of intermediate hosts and supplementary hosts in the pond; people have more opportunities to eat fresh fish, and they like to eat "fish"; cats and dogs A wide range of activities, eating raw fish, these constitute a prevalent factor in this disease. [Pathogenic effect] The worms are parasitic in the bile duct and gallbladder of the animal. Due to mechanical stimulation, the bile duct and gallbladder are inflamed, the wall is thickened, and the digestive function is affected. The worm secretes toxins, causing anemia, weight loss and edema. When a large number of parasitic, the worm block the bile duct, causing bile secretion and yellow biliary phenomenon. After a long period of parasitism, liver connective tissue hyperplasia, hepatocyte degeneration, atrophy, capillary bile duct embolization, causing cirrhosis. Human schizophrenia is closely related to cholangiocarcinoma. [pathological changes] The main lesions in pigs and dogs are in the liver and gallbladder. The gallbladder is enlarged, the bile duct becomes thick, the bile is thick, and the grass is green. There are many worms and eggs in the bile duct and gallbladder. Connective tissue hyperplasia on the surface of the liver, sometimes causing cirrhosis or fatty degeneration. ã€symptom】 Severe infection, dyspepsia, loss of appetite and diarrhea, and finally anemia, ã€diagnosis】 If in the epidemic area, there is a habit of feeding pigs with raw fish and shrimp, such as clinical symptoms of indigestion and diarrhea, you can suspect the disease, such as the detection of eggs in the feces can be diagnosed. The method of inspection is better by the method of floating eggs, and the detection rate of the centrifugal floatation method is the highest. In recent years, immunological methods such as indirect hemagglutination test and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay have been used for auxiliary diagnosis. ã€treatment】 The following drugs are available: (1) piperazine propionate, according to 50 ~ 60mg / kg body weight, mixed into the feed to feed, once a day, 5 days for a course of treatment. (2) albendazole, according to 30 ~ 50mg / kg body weight, once orally or mixed feed. (3) Praziquantel, once orally, at a dose of 10 to 35 mg/kg body weight. ã€prevention】 1. Pigs, dogs and cats in popular areas are subject to comprehensive inspection and deworming. 2. It is forbidden to feed animals with raw or undercooked fish and shrimp in the affected areas. 3. Strengthen the management of manure to prevent manure from contaminating the pond. It is forbidden to cover the pig house or toilet in the fish pond. 4. Eliminate the first intermediate host freshwater snail, which should be captured or buried. GMP ATS Injection, Tetanus Antitoxin, Tetanus Toxoid ,Tetanus Antitoxin Injection, Antitetanus, Refined Tetanus Antitoxinsupplier in China Tetanus Antitoxin,Tetanus Toxoid,Tetanus Antitoxin Injection,Antitetanus&Refined Tetanus Antitoxin FOSHAN PHARMA CO., LTD. , https://www.fs-pharma.com