"Seven Key Factors" in Cancer Immunotherapy
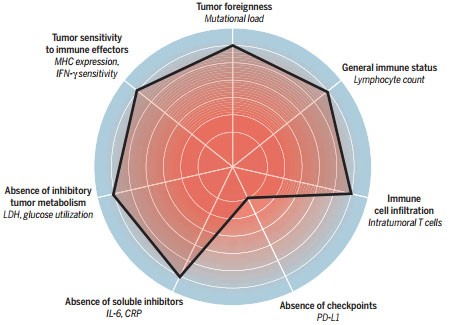
The impact of immunotherapy on clinical cancer treatment is rapidly increasing. However, different immunotherapies address different issues in cancer-immune system interactions. So, which treatment is most effective for each patient? On May 6th, in an article published online in Science entitled "The cancer immunogram," the authors propose a framework for the interaction between cancer and the immune system in individuals. Their goal is to focus on biomarker research to help guide treatment options. The results of cancer immune interactions depend on a large number of parameters, such as T cell inhibition mechanisms; the "values" of these parameters vary widely from patient to patient. Based on the multifactorial properties of cancer-immune interactions, the combined use of biomarker detection has become an inevitable need. The cancer immunogram (Source: Science) The Cancer Immunogram proposed in this article assumes that T cell activity is the ultimate mechanism of action in human tumors. This in no way means that the inhibition of tumor-associated macrophages, the regulation of the microbiome, and the like are of no value. The authors hypothesized that the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy ultimately correlated with enhanced T cell activity. Future research will verify that this assumption is correct. The authors also acknowledge that their understanding of cancer-immune interactions remains incomplete. In the future, new biomarkers may be added, and some existing markers may be removed. The following seven parameters are included in this initial framework: 1) Tumor foreignness The results of "meeting" of T cells with antigen are regulated by T cell checkpoints, such as CTLA-4, PD-1. Recent studies have shown that the "foreignness" of human cancer is largely determined by the expression of its neoantigens. The PD-1 inhibitory activity in DNA mismatch repair is also associated with the "foreignness" of the tumor, which is also a determinant of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. The authors say that although the “foreignness†of the tumor may be guaranteed in tumors with very high mutation loads, in the case of moderate or low levels of mutational load, the “foreignness†of the tumor can only be inferred, so more is needed. Interpretation of this aspect. Innovative jet embedded nylon technology maximizes the efficiency of sample collection from patients. Nylon adheres vertically and evenly to the surface of the swab tip, improving the efficiency of cell and liquid sample collection and release. Increased analytical sensitivity, no specimen residue, and accelerated specimen processing. Flocked Swab,Collect swabs from specimens with flocked tips,Medical sampling swab oral nylon swab flocking,Acts in the clinical diagnosis Jiangsu iiLO Biotechnology Co., Ltd. , https://www.sjiilogene.com