Common laboratory waste treatment
In view of the complex types of waste liquids in the laboratory, the high concentration of one type of pollutants, the high concentration and the small amount of water, the principles of classified treatment and quality treatment are followed. The laboratory waste liquid is first divided into organic waste liquid and inorganic waste liquid. Two major categories. The inorganic waste liquid contains cyanide, heavy metal waste liquid, etc.; the organic waste liquid contains waste liquid of chloroform, carbon disulfide, carbon tetrachloride and integrated organic waste water. On this basis, a method for separately treating waste liquid is proposed. 1 organic waste liquid 1.1 Chloroform (chloroform) waste liquid In the analysis of arsenic (DDC-Ag spectrophotometry), volatile phenol (4-aminoantipyrine extraction spectrophotometry), anionic detergent (methylene blue spectrophotometry) and other items are used chloroform, colorimetrically followed by chloroform Waste liquid: It is highly toxic and cannot be dumped at will. It should be dumped in the designated “chloroform waste liquid collection tank†for recycling. The following picture shows the process: Carbon disulfide is used for the analysis of benzene series (carbon disulfide extraction, gas chromatography). After the analysis, a certain carbon disulfide-containing waste liquid is produced. It is highly toxic and cannot be dumped at will. It should be poured into the designated “carbon disulfide waste liquid barrelâ€. Recycling, the following picture shows the process: 1.3 Containing carbon disulfide waste liquid In the work of water pollution source supervision and detection, total quantity monitoring, etc., the remaining high concentration integrated organic wastewater in the laboratory analysis is poisonous and cannot be dumped at will. It should be concentrated in the “comprehensive organic waste liquid barrel†and regularly send nearby wastewater. Plants with similar properties and well-established wastewater treatment facilities are treated together with plant wastewater. 2 organic waste liquid 2.1 Cyanide-containing waste liquid For cyanide project analysis, cyanide standard solution, intermediate solution and use solution should be prepared. The standard curve is prepared. The used liquid must be used on the same day of the day. The remaining cyanide liquid cannot be dumped at will because it is highly toxic. It should be poured into the designated “cyanide waste tankâ€. The process is shown in the following figure: 2.2 Heavy metal waste liquid The above is only some of the author's practice and discussion on the common waste liquid treatment in the laboratory; to do this work well, the whole society needs to cooperate together, and it is our habit for safety! ! The BPAP System makes a good performance in Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICU) and other departments. Offer you the choices you need in ventilation, monitoring and technique. what`s more, our expertise in ventilation is based on rich 23-year history of developing BPAP solutions that meet your needs. Good performance based on High Security, High Accuracy, High Stability and accurate monitoring. BPAP 30,Ventilator Non Invasive,Non Invasive Ventilation Equipment,Non Invasive Vent Equipment Shenyang RMS MEDICAL TECH CO.,LTD , https://www.medicalrms.com
As the degree of scientific management of environmental management continues to increase, the requirements for environmental monitoring are also increasing. Environmental monitoring is constantly expanding the field of monitoring and improving its ability to serve environmental management. While environmental monitoring provides technical support for environmental management, the laboratory produces a number of toxic and hazardous analytical waste streams. The toxic and hazardous waste liquid in the laboratory must be classified and prevented, handled properly, and cannot be dumped at will; however, there is no complete laboratory waste treatment method. 
1.2 Containing carbon disulfide waste liquid 
The analysis of mineral oil (carbon tetrachloride extraction, infrared oil spectrophotometry) project uses carbon tetrachloride. After the analysis, a certain amount of carbon tetrachloride waste liquid is produced. It is highly toxic and cannot be dumped at will. It should be poured in the designated In the “CTC waste liquid barrelâ€, the recycling process is carried out, and the process is shown in the following figure; when the first rectification is carried out, wrapping the package with a damp cloth can increase the rectification speed. 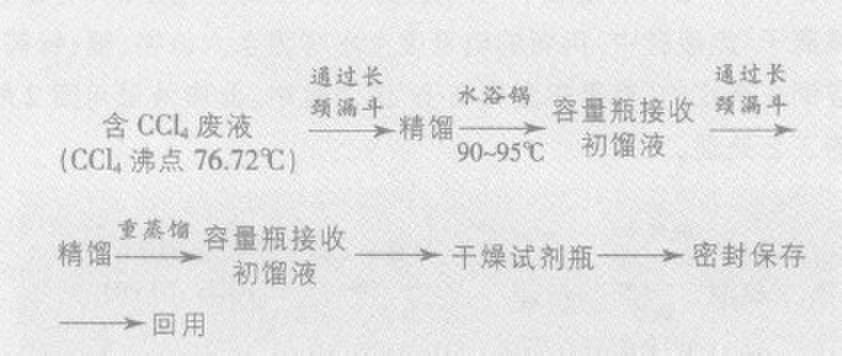
1.2 Integrated organic wastewater 

