Chinese scholar Cell discovers new functions of macrophages
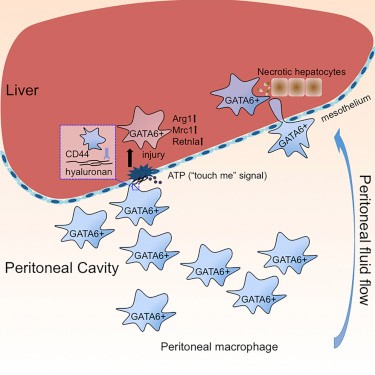
Although scientists have known for many years that cells live in various tissues such as the heart, lungs, and liver, the function is still unclear. A recent study by the Cumming School of Medicine at the University of Calgary in Canada examined these cells and found them to play an integral role in rapid tissue repair. The study was published this month in the journal Cell. In several types of immune cells present in body cavities, the study specifically looked at macrophage, which plays a key role in the removal of harmful organisms and microorganisms such as toxins and bacteria, and the elimination of dead tissue. By observing cells in the peritoneal cavity surrounding the liver, this study confirmed that macrophages patrol the cavity, and once the organ is damaged, the macrophage will adhere itself to the damaged area for rapid repair. Dr. Jing Wang, a lead author of the study and a member of the Snyder Institute for Chronic Diseases, said: "The traditional view is that the repair process of damaged organs is: recruitment of monocytes (an immune cell in the blood) At the site of injury, monocytes leave the blood vessels and mature into macrophages within 2-3 days. In our study, mature macrophages are already present in the cavity and can directly penetrate into the damaged parts of the internal organs. , thereby enabling direct and quick fixes." Using animal models, the researchers used live imaging techniques to view these cells in real time and observed their behavior in response to thermal damage and toxin-induced damage. These cells treat both lesions in the same way. It was further observed that tissue repair did not occur rapidly when the macrophage supply was depleted in the abdominal cavity. When cells are returned to the animal model, they continue to play their role. Wang Jing said that although this study only looked at these cells in the abdominal cavity and how they respond to liver damage, there is still reason to speculate that other body cavities, such as the pleural cavity around the lungs, and the cells in the pericardial cavity around the heart, can be performed. Similar features. Although the study was done in animal models, Wang Jing said the study may also have implications for humans. "Humans have the same body cavity as mice, so we infer that the same cells perform the same function in our bodies." Wang Jing continues, this finding may have special implications for clinical procedures and procedures that typically “clean†the relevant body cavity to remove exogenous pathogens. This study suggests that doing so may actually hinder the healing process by depleting macrophages in the body cavity.
The lock channel is one of the most important thing for greenhouse, it can lock the film ,shading net ,insect net .
It is hot galvanized or aluminum material.
We have different thickness.
Welcome to contact us
GREENHOUSE Lock Channel,Greenhouse Lock Channel,Channel Lock,greenhouse profile JIANGSU SKYPLAN GREENHOUSE TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.greenhousehydroponic.com